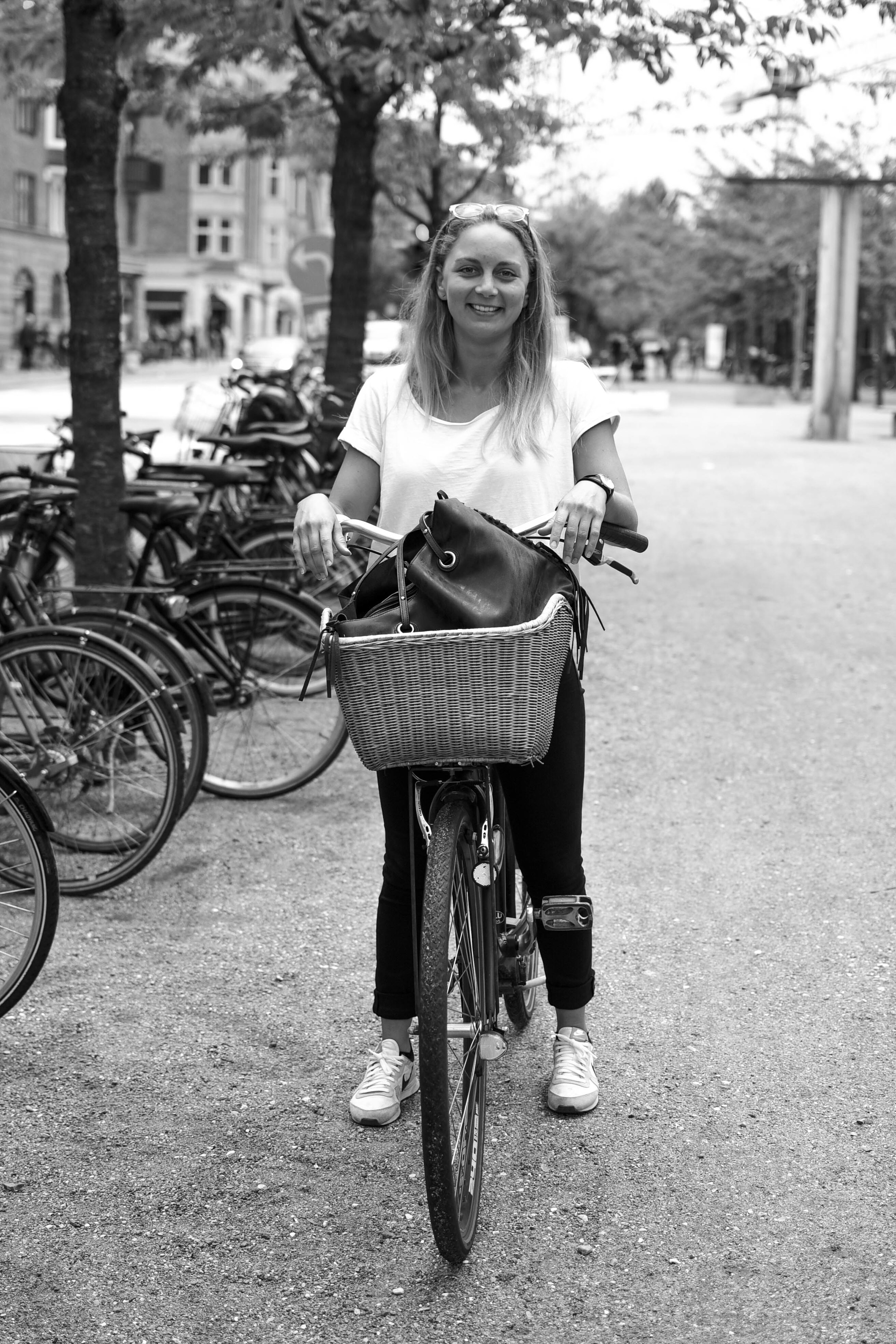Everyone knows that Copenhagen is the happiest city in the world. But not as many people appreciate just how unique and interesting it is. As a regular visitor, below I've listed out my top reasons why Copenhagen is the world's coolest city.
Vibrant Neighbourhoods
Nørrebro
Norrebo is one of Copenhagen's trendiest districts: people look amazing, bars and cafes line the streets, and its energetic vibe lasts late into each night.
But this neighbourhood's vibrancy isn't simply a coincidence - Norrebro is the city's most multicultural area. With 26% of its inhabitants from outside of Denmark, it offers an incredible cultural mix of food, music, language and fashion-styles.
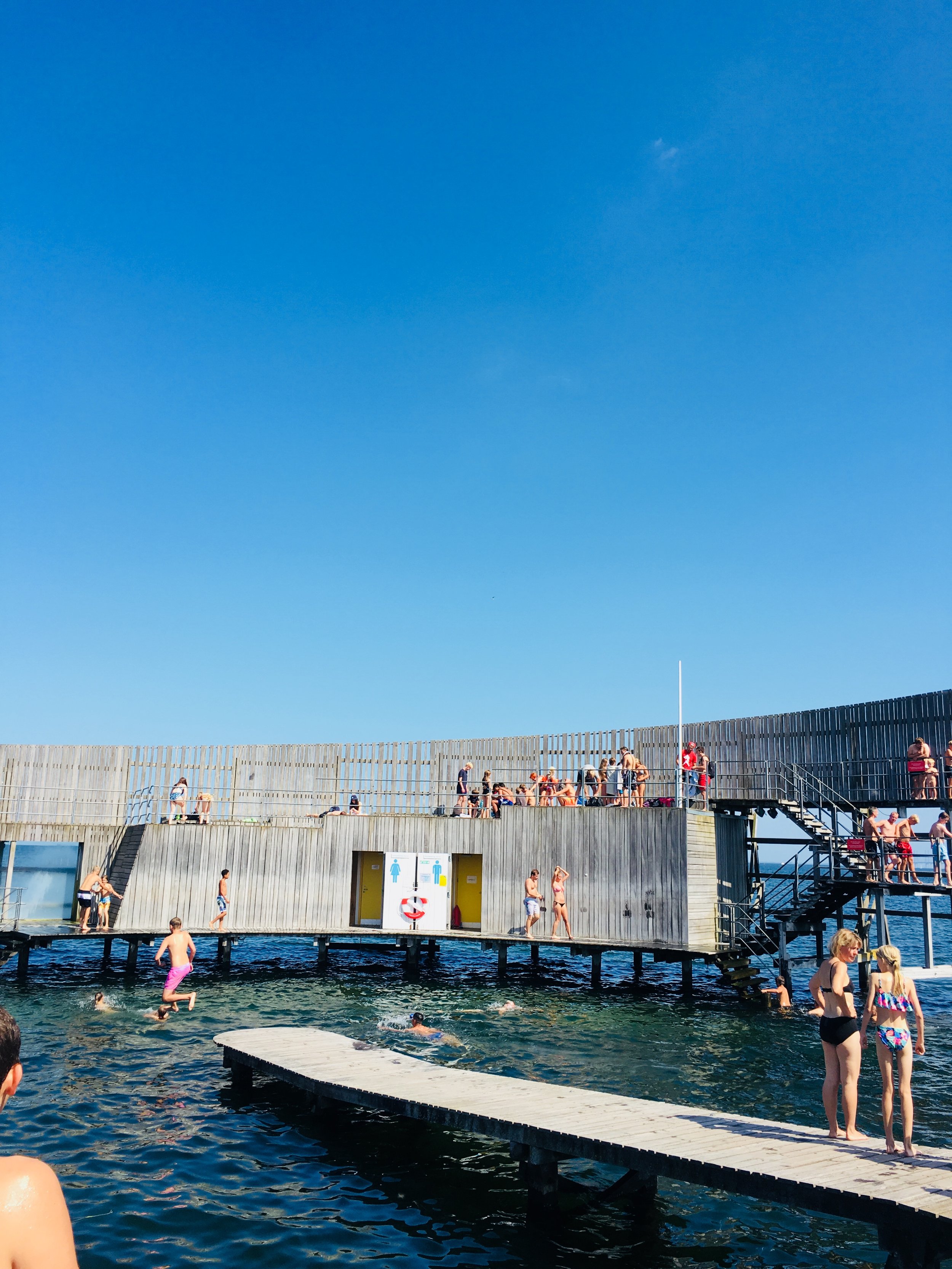
Islands Brygge
In contrast to the eclectic urban vibe of Norrebo, Islands Brygge is predominantly residential. But what makes this one of my favourite parts of the city, is its harbourside location and incredible stretches of open space.
Differently to most cities around the world, Copenhagen's government is liberal enough to let people swim in its harbour, and there's probably no better place to do that than Islands Brygge.
In summertime this neighbourhood is crowded with swimmers, drinkers, skaters and chillers - all checking out the beauty of the city... and probably each other. There's no doubt that this is where some of Copenhagen's most attractive people come for some time in the sun.
MeatPacking District (Kodbyen)
Much like New York City's Meatpacking District, Copenhagen's old cattle markets have seen a recent rejuvenation, as young people embrace its large open spaces and old industrial buildings.
While parts of the district are still used for the meat industry, since the early 2000s it's also emerged as a creative cluster, attracting galleries, restaurants, design firms and studios.
I recommend grabbing a coffee or beer and simply wandering around the district's streets; the mix of large, small, old and new buildings provide for a seemingly never-ending maze of beautiful hidden streetscapes.
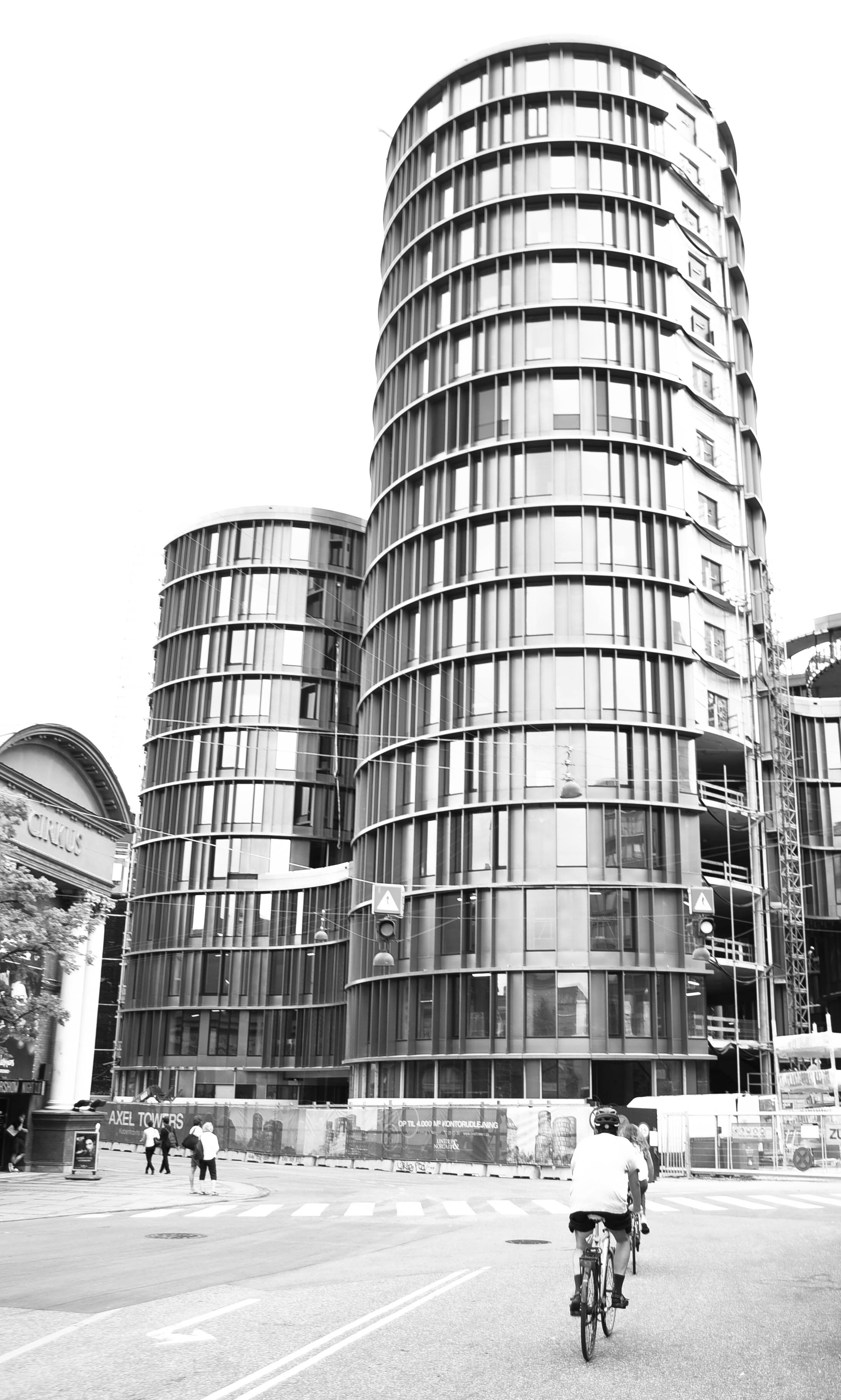
Architecture
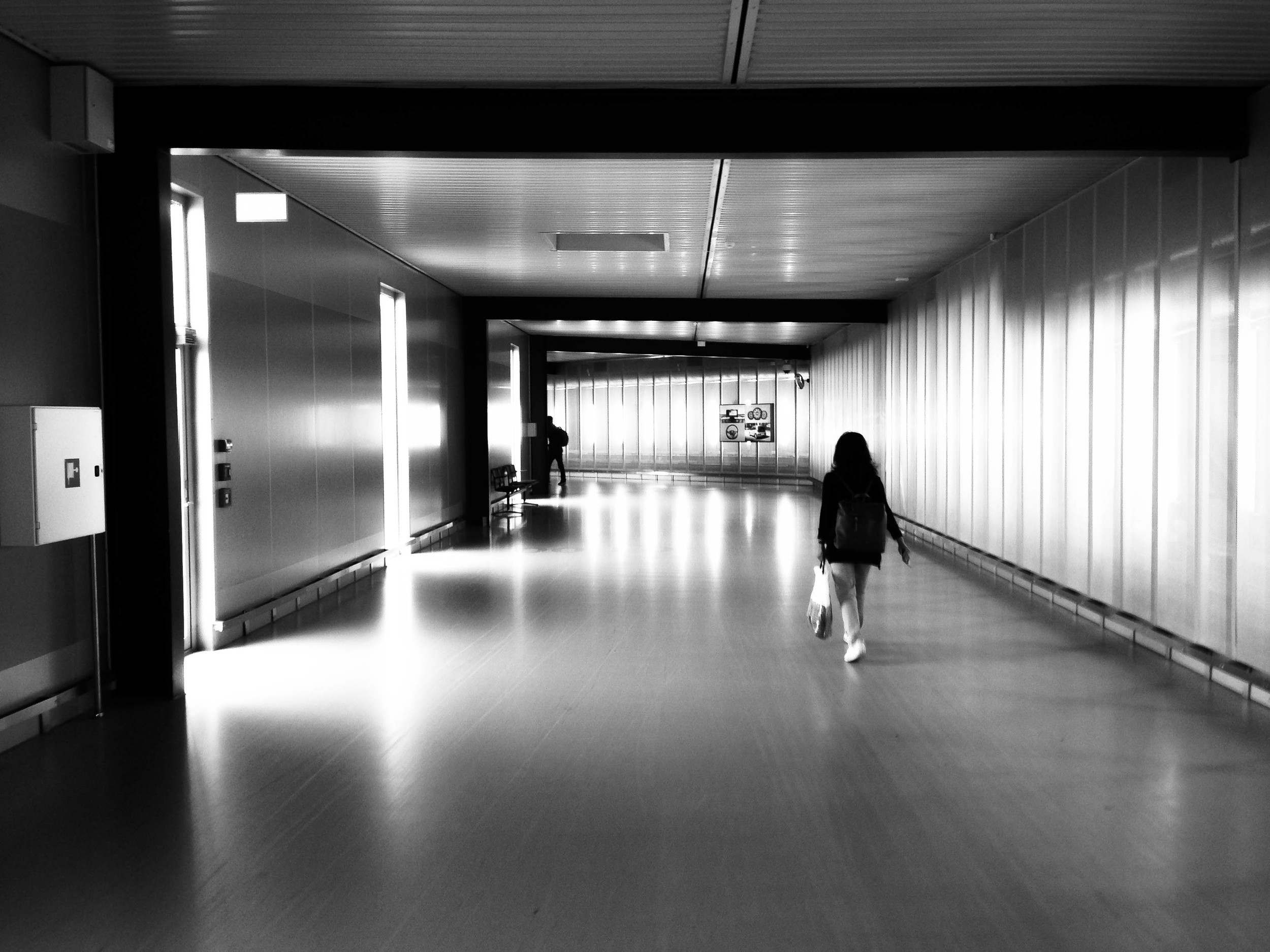
As soon as you step off the plane into Copenhagen's Kastrup Airport's beautifully designed terminals, you'll realise that this is a city that prides itself on clean, human-focused architecture.
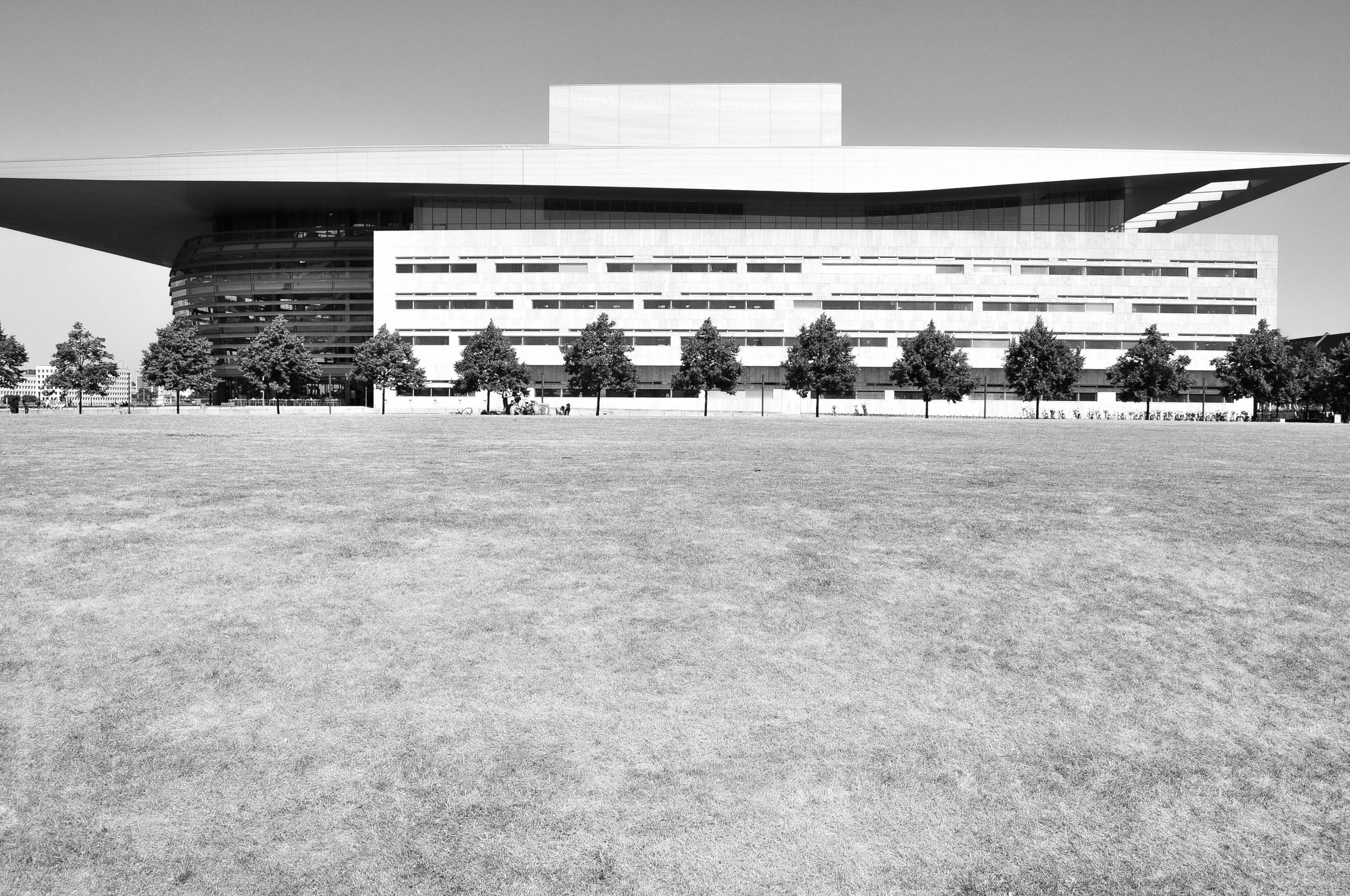
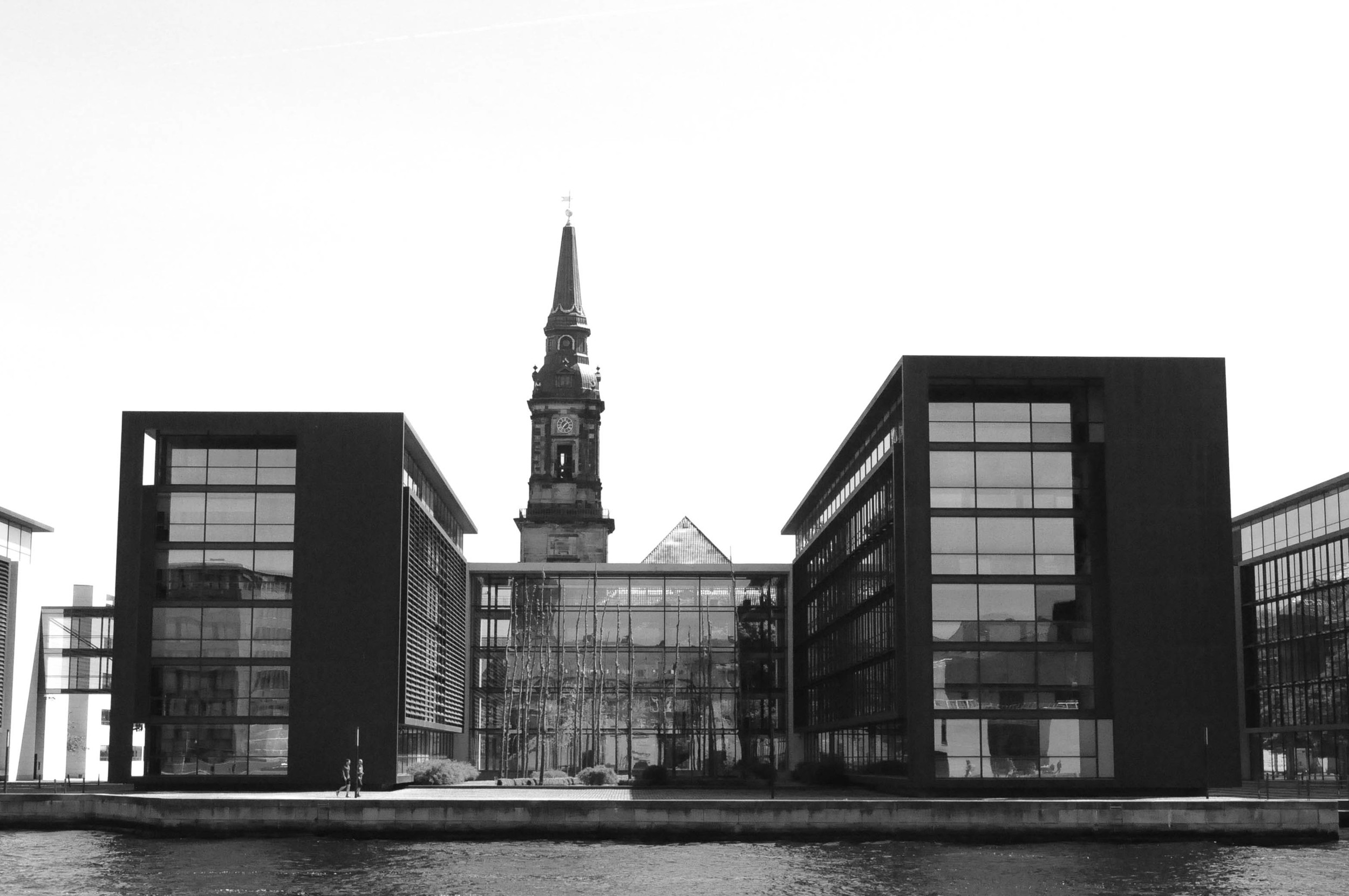
It's buildings comprise a full range of styles, all the way from the 17th century. In my opinion, however, it's the contemporary buildings which are some of the best: the Copenhagen Opera House and the Axel Towers to name just two.
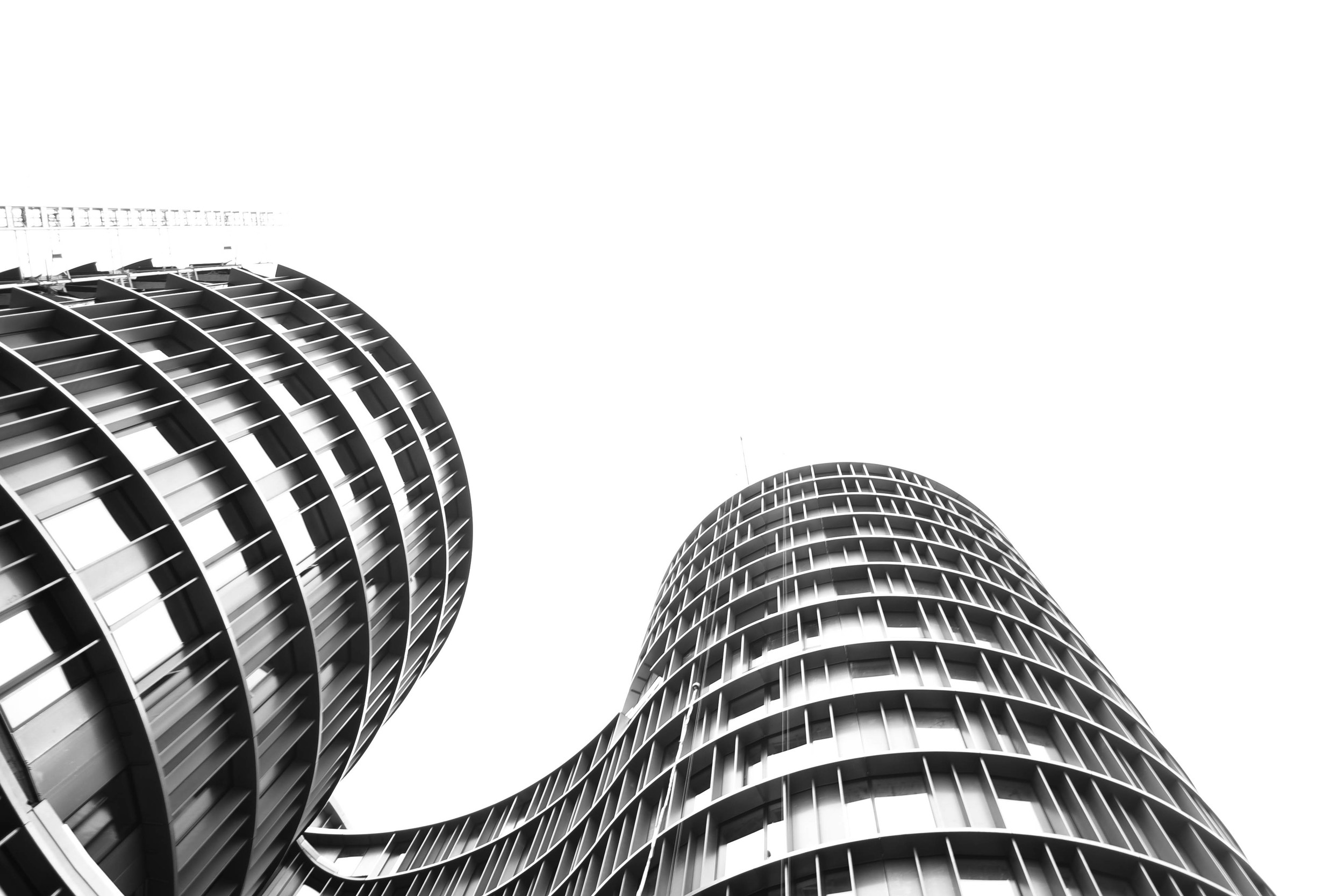
Unlike the tall and bulky buildings in the US, Asia and the Middle East, Danish designers tend to focus on the details, such as fine shapes, curves and materials. As a result, the city has avery soft, and even feminine, feel to it.
But my love for Copenhagen architecture is as much about the spaces between the buildings, as it is the buildings themselves. People here are not pushed to the edge of streets to make way for cars, and public spaces are not simply an urban designer's afterthought. This is a city where buildings have been shaped around open spaces - not the other way around.




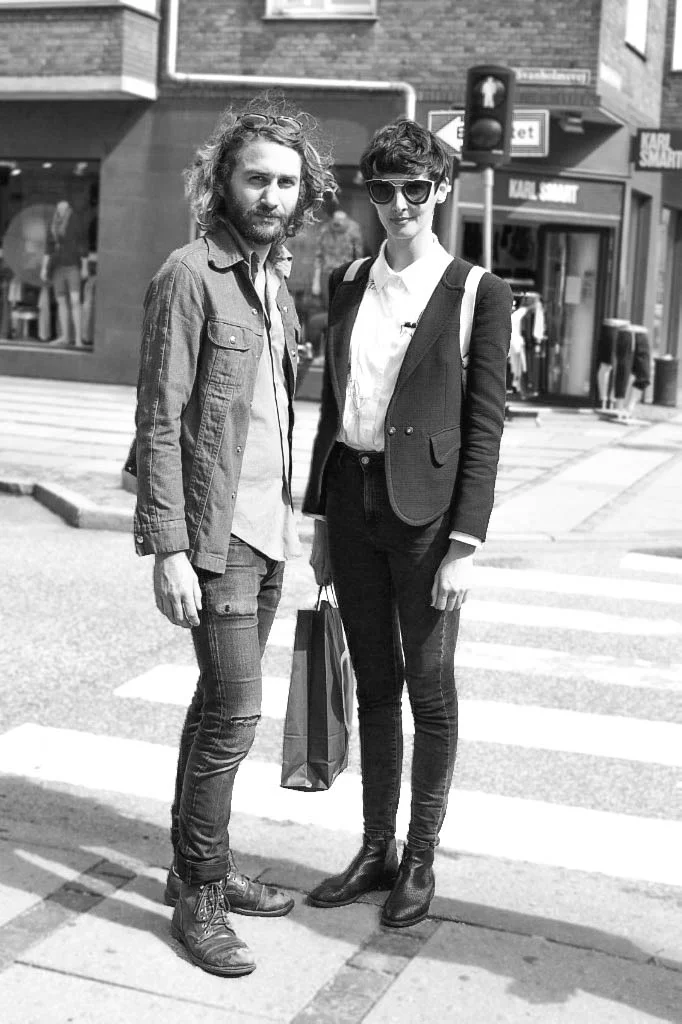
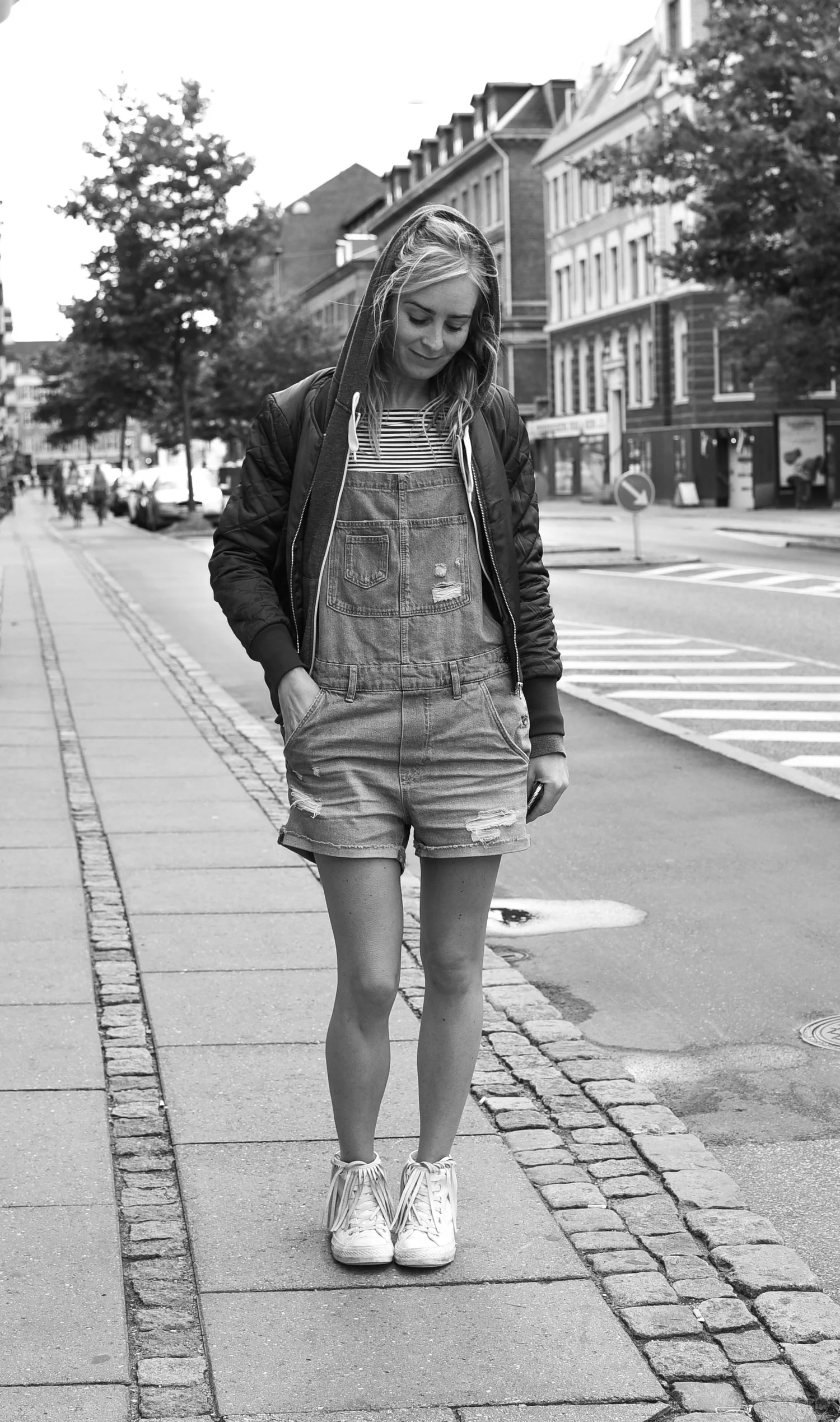
Fashion
Copenhageners are a stylish bunch of people, but not in some 'edgy' up-your-own-ass-east-London kind of way. Instead, just like Copenhagen's architecture, nice design seems to be deeply embedded into Danish culture.
People on the street - young and old - have a generally distinctive Danish look: cuts are low and slouchy and logos are minimal. And even those who mix it all up and do something totally different still tend to look classy and timeless.
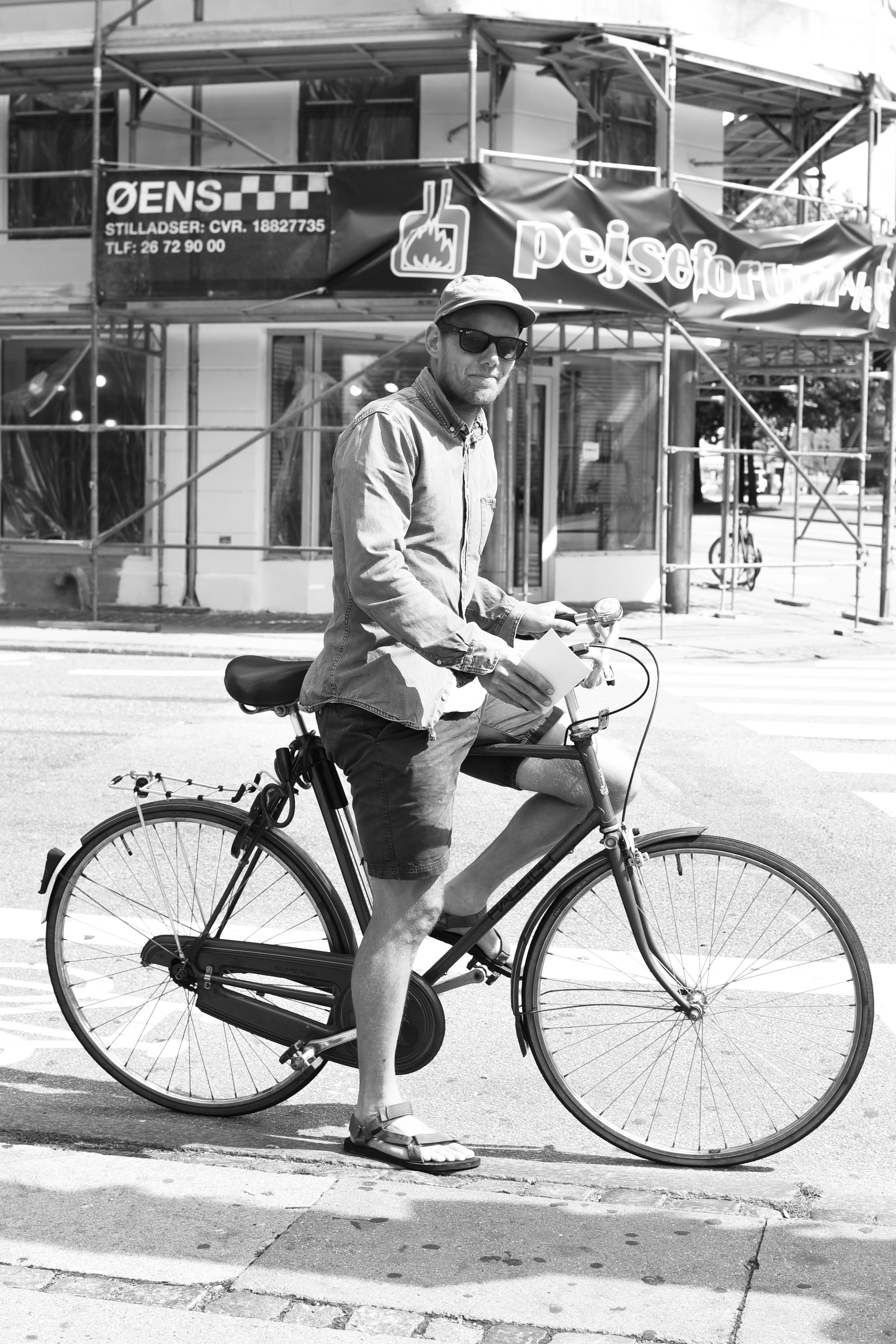
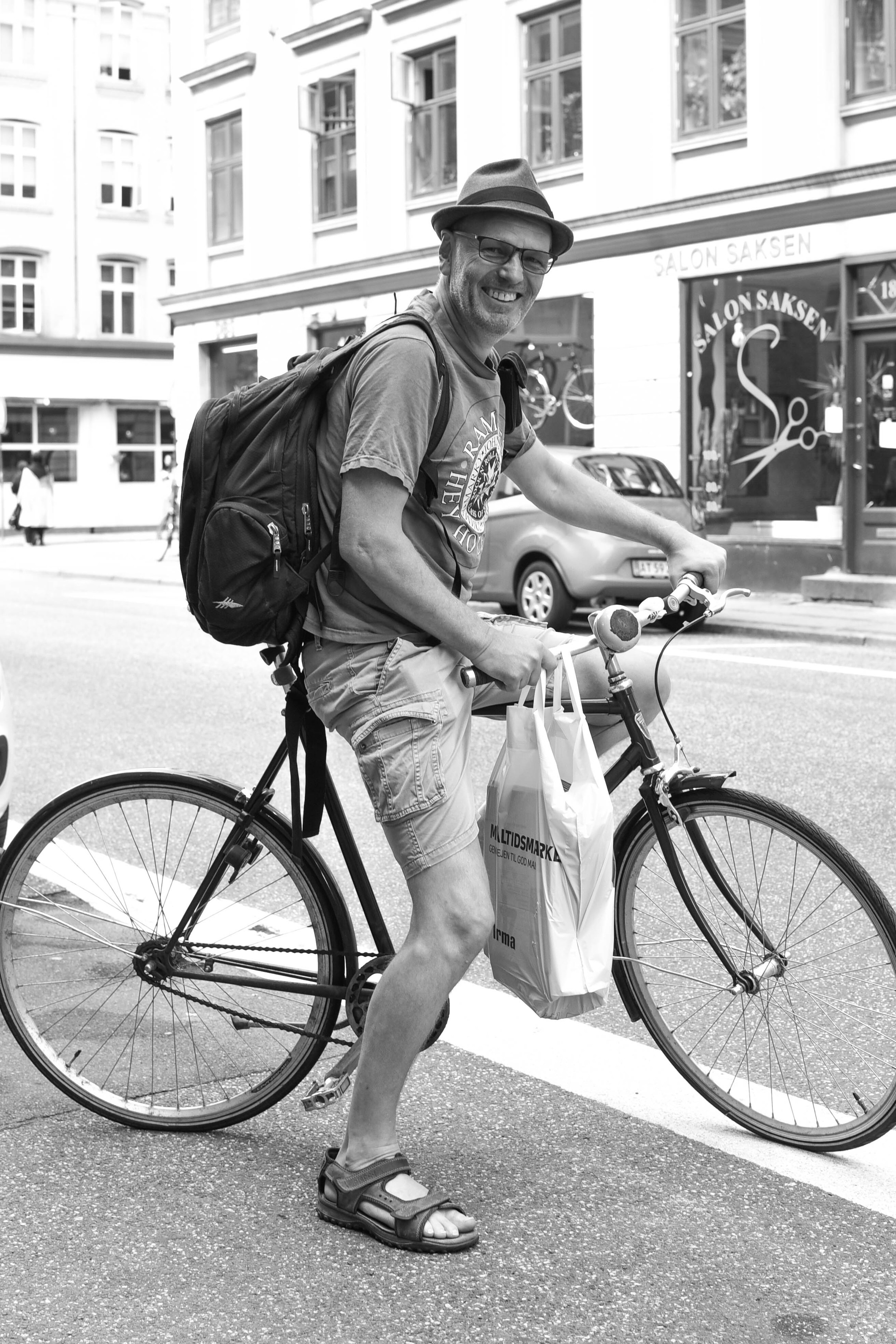
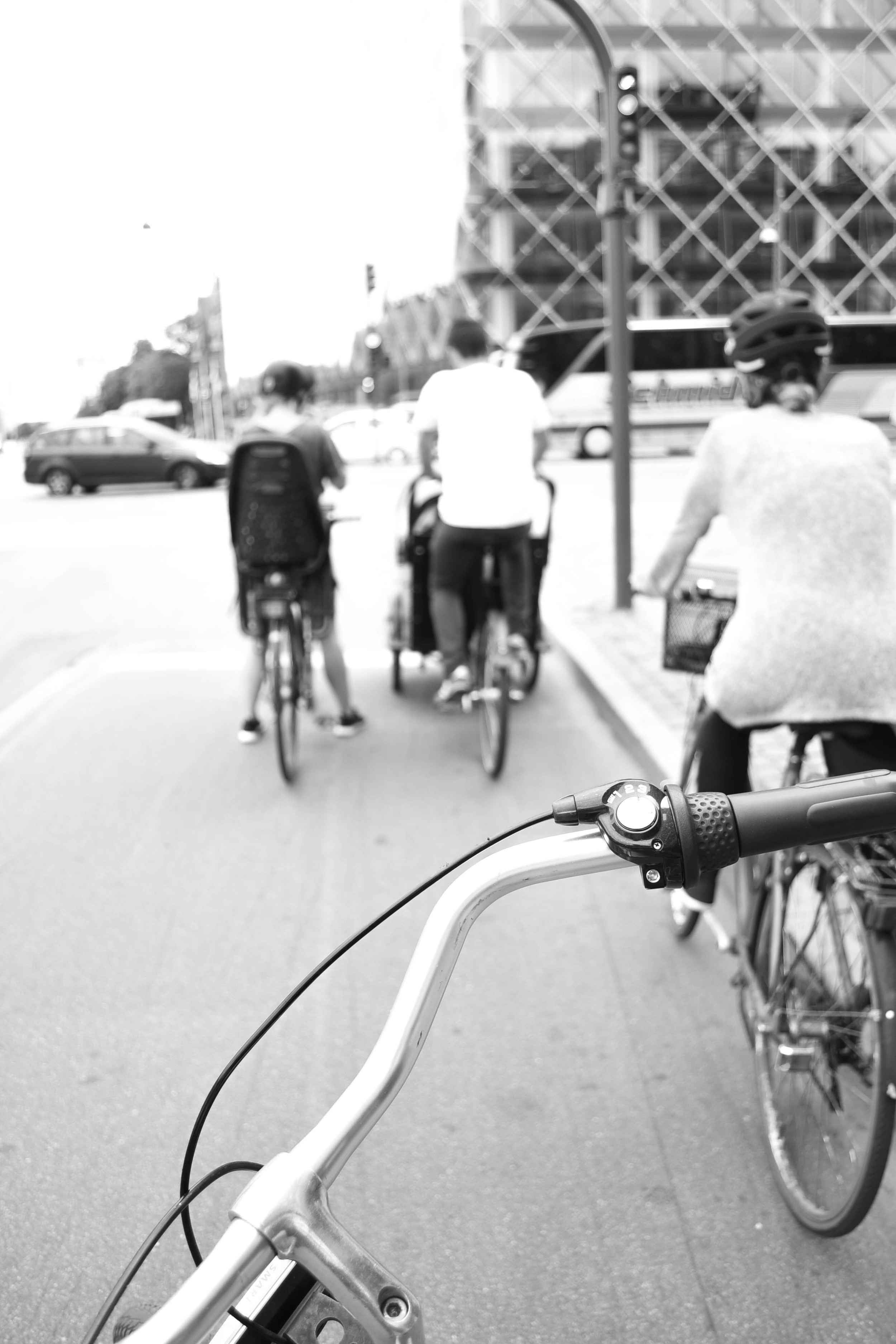
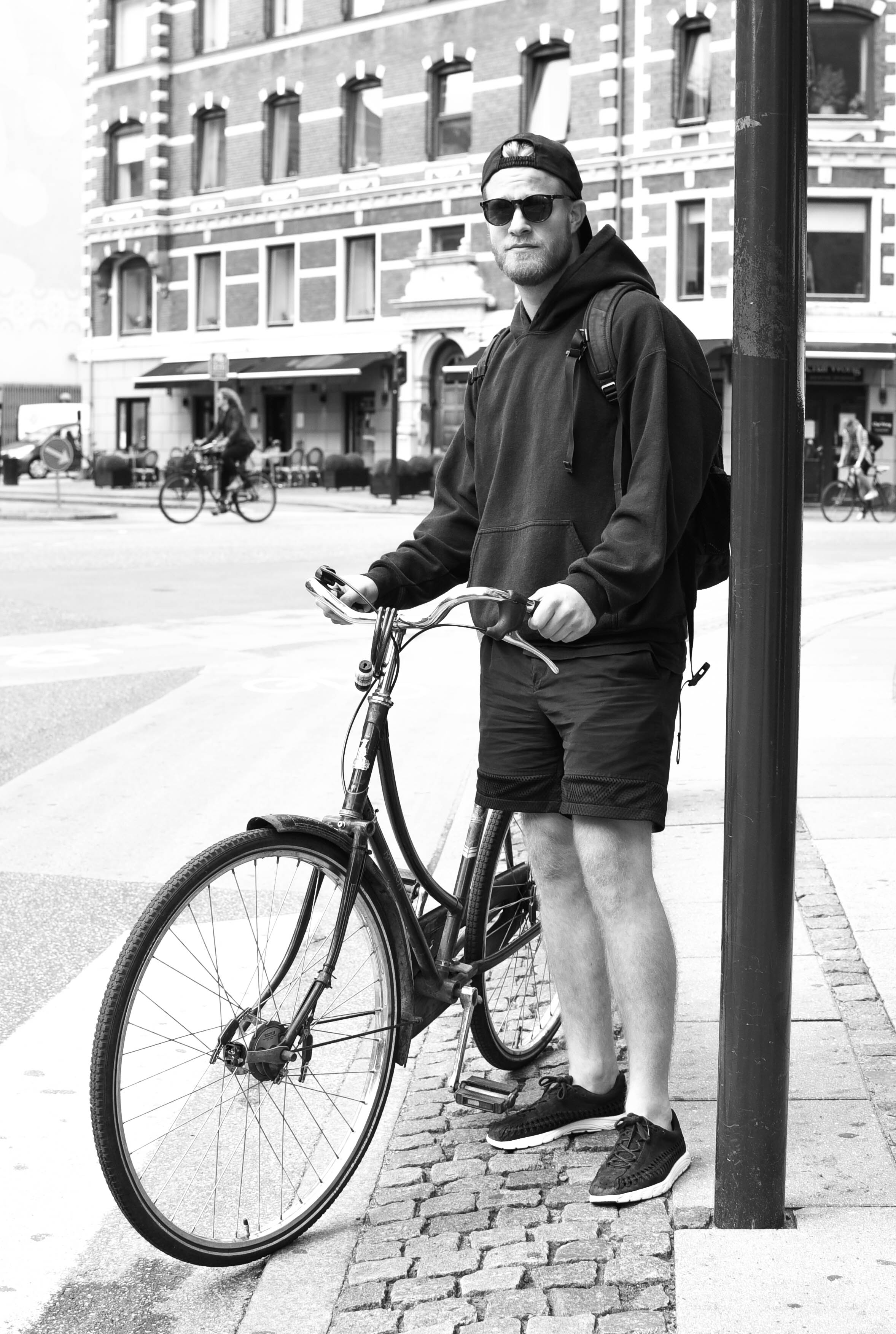
The love for bikes
It'd be virtually impossible to write a post on Copenhagen without a mention of bicycles.
As soon as you step foot in the city, you'll notice that just about everyone is on two wheels. But riding in Copenhagen is not about being a 'cyclist': it's not about lycra, helmets, bells, or reflectors. Bike riding in Copenhagen is about function, mixed with a bit of your own personal style.
With lanes separating bikes from cars, moving through the city is a stress-free experience. It won't take you long to realise that every place in the world really should Copenhagenize.